Finasteride (marketed by Merck under the trademark name Propecia) is a synthetic antiandrogen that acts by inhibiting the enzyme that converts testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT). Finasteride significantly reduces DHT, a key cause of hair loss, by inhibiting the formation of DHT in your scalp. Lowering DHT appears to inhibit the continued shrinking of affected hair follicles.
DHT’s Roll in Hair Loss
 Both men and women tend to lose hair due to some hormonal changes in the body. It is mainly the alterations in the metabolism of androgen in the body that brings about hair loss.
Both men and women tend to lose hair due to some hormonal changes in the body. It is mainly the alterations in the metabolism of androgen in the body that brings about hair loss.
The most important structure of a hair follicle is the dermal papilla, which is responsible for hair growth. The dermal papilla lies in direct contact with capillaries in the skin and is responsible for deriving nutrients needed for hair follicle growth.
When DHT reaches the hair follicles and dermal papilla, it tends to prevent vitamins, minerals and proteins from nourishing the hair follicles. When this occurs, hair follicles will 1) reproduce at a slower rate, 2) will also shrink (or thin).
Men and women who are genetically pre-disposed to hair loss produce more DHT than others.
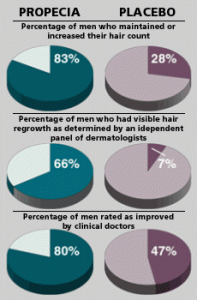
Clinical Data
Finasteride was initially approved by the FDA in 1992 under the brand name Proscar, a treatment for benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). In 1997, the FDA approved finasteride to treat male pattern baldness (MPB) under the brand name Propecia.
In a 5-year study of men with mild to moderate hair loss, two-thirds of the men who took Propecia daily regrew hair (as measured by hair counts). In contrast, all of the men in the study who were not taking Propecia lost hair. In the same study, 48% of those treated with Propecia experienced visible hair growth, and a further 42% had no additional hair loss.
Propecia is effective only for as long as it is taken. Any gains in hair count will be lost six to twelve months of stopping therapy. Propecia, like Rogaine, is effective on the crown area and the hairline, but is most successful in the crown area.


 "Hair Science received high marks from the team at Bosley.
"Hair Science received high marks from the team at Bosley.


